Moving Resources Between CDK Stacks with Stack Refactoring
Update (September 2025): CDK now has built-in support for refactoring stacks. Use that before attempting anything described below.
Last week, AWS announced the availability of a new feature in CloudFormation called “Stack Refactoring”. This feature is one which addresses one of the biggest weaknesses in CloudFormation in my opinion: state management. It allows you to refactor your CloudFormation stacks by moving resources between stacks after they have been deployed. This is a boon for breaking up monolithic stacks, separating concerns, or just improving maintainability of your stacks as your project grows.
Previously, there were some very manual ways to achieve this functionality. You could set the deletion policy on the resources in your old stacks, remove the resources, and then do the reverse on your new stack and import the resource. But this process was very manual and had a high potential of error. Fortunately, with the introduction of Stack Refactoring, moving resources between CloudFormation Stacks can be completed in a much easier way.
That said… having this feature in CloudFormation is great and all, but these days I pretty much exclusively work with CloudFormation via CDK, so I wanted to take some time to see how Stack Refactoring fits into the CDK workflow. It required a little bit of massaging to get it all working, but once I had everything prepared correctly the refactor worked just fine in CDK. This post will walk you through my experiences using Stack Refactor with CDK and hopefully help you avoid some of the same issues I had along the way.
If you just want to know the essentials, skip to the tl;dr.
CDK Stack Refactor Walkthrough
This example is a pretty simple one. We’ll start with a single CDK stack which creates an EC2 instance and an S3 bucket. After the resources are created, we will perform a refactor and move the S3 bucket to a separate stack. Here’s an overview of the steps we’re going to take:
- Deploy the “before” stack. In the real world, you have likely already done this step.
- Create the new stack in CDK with the resource to be migrated and remove it from the old stack.
- Create a mapping file for the refactor and submit it to the CloudFormation API
- Execute the refactor
The process is relatively straightforward, but there are a few gotchas when doing a stack refactor with CDK that I hope I can help you avoid. I’m going to be creating a new stack as a part of the refactor process, which means CloudFormation will create the new stack when I execute the refactor step. But this process will also work – with a few modifications – if you have two stacks which are already deployed and you just want to move a resource between them.
Step 1: Preparing the “Before” Stack
Here’s what the “before” stack looks like: a single CloudFormation stack with an EC2 instance, S3 Bucket, and IAM role.
// lib/stack-refactor-stack.ts
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import * as ec2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2'
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3'
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'
import { Construct } from 'constructs'
export class StackRefactorStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
// We're going to move this Bucket to the new stack
const bucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'Bucket', {
bucketName: 'a-very-special-bucket-123',
})
const role = new iam.Role(this, 'IamRole', {
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal('ec2.amazonaws.com'),
})
bucket.grantWrite(role)
role.addManagedPolicy(iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName("AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore"))
const vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, 'Vpc', {
maxAzs: 2,
})
const securityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, 'SecurityGroup', {
vpc,
description: 'Allow only outbound internet access',
allowAllOutbound: true,
})
const instance = new ec2.Instance(this, 'Instance', {
vpc,
instanceType: ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T2, ec2.InstanceSize.MICRO),
machineImage: ec2.MachineImage.latestAmazonLinux(),
securityGroup,
role,
})
}
}
If you already have this stack deployed, great. However, the first gotcha which you’ll run into is that Stack Refactoring does not support certain resources in CloudFormation. And by default, every deployed CDK stack will include AWS::CDK::Metadata resources which are not supported. Here’s an example error which you’ll see if you start the refactor process with these resource in your stack:
{
"StackRefactorId": "7c6f0da3-eb89-44ef-bd40-c63b6627d11c",
"StackIds": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/StackRefactorStack/fd2b1b20-e7cc-11ef-a316-06ca57e568d9",
"arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/BucketStack/31e55930-e7d1-11ef-90e2-0a407e496199"
],
"ExecutionStatus": "OBSOLETE",
"ExecutionStatusReason": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/StackRefactorStack/fd2b1b20-e7cc-11ef-a316-06ca57e568d9: Stack was updated.",
"Status": "CREATE_FAILED",
"StatusReason": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/StackRefactorStack/fd2b1b20-e7cc-11ef-a316-06ca57e568d9: Stack Refactor does not support AWS::CDK::Metadata."
}
So the first thing you should do if you already have your “before” stack deployed is to not change anything in the stack, and pass flags to cdk deploy to remove unsupported resources.
cdk deploy --version-reporting=false --path-metadata=false --asset-metadata=false
This will redeploy your stack without the metadata resources and allow you to create the stack refactor. Once you’re done with the refactor, you can deploy the CDK stack as you normally would without these flags.
If you’re still seeing this error even after redeploying your “before” stack, check the template definition as deployed in CloudFormation, and make sure you don’t see any metadata in the template. One thing which I found was that CloudFormation would report that the stack was correctly deployed, but since there were no physical resource changes in my template, it never actually removed the metadata. So I just made a meaningless change to a resource (I updated the description on my Security Group), redeployed, and then it worked.
Step 2: Moving the resource in CDK
Okay, now that we have prepared the “before” stack, let’s move the S3 Bucket to a new stack. There’s another gotcha here: stack refactors when you are creating the new stack as a part of the refactor do not support Condition or Rule resources, so we’ll need to make some modifications to how our new stack is synthesized in order to avoid creating these resources. I cover how to do this below.
New “Bucket” Stack
// lib/bucket-stack.ts
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3'
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'
import { Construct } from 'constructs'
export interface BucketStackProps extends cdk.StackProps {
allowedPrincipal: iam.IGrantable
}
export class BucketStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props: BucketStackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
const bucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'Bucket', {
bucketName: 'a-very-special-bucket-123',
})
bucket.grantWrite(props.allowedPrincipal)
}
}
Updated “Refactor” Stack
// lib/stack-refactor-stack.ts
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import * as ec2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2'
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam'
import { Construct } from 'constructs'
export class StackRefactorStack extends cdk.Stack {
public readonly instanceRole: iam.Role
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
const role = this.instanceRole = new iam.Role(this, 'IamRole', {
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal('ec2.amazonaws.com'),
})
role.addManagedPolicy(iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName("AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore"))
const vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, 'Vpc', {
maxAzs: 2,
})
const securityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, 'SecurityGroup', {
vpc,
description: 'Allow only outbound internet access',
allowAllOutbound: true,
})
new ec2.Instance(this, 'Instance', {
vpc,
instanceType: ec2.InstanceType.of(ec2.InstanceClass.T2, ec2.InstanceSize.MICRO),
machineImage: ec2.MachineImage.latestAmazonLinux(),
securityGroup,
role,
})
}
}
Adding the “Bucket” Stack to cdk.App
If you have an existing “destination” stack for the refactor, you can probably skip this step.
Stack Refactors don’t support Condition or Rule resources in templates when the refactor is creating a new stack. By default, CDK stacks create both Conditions and Rules, so you’ll need to make some changes to how the stack is synthesized by setting generateBootstrapVersionRule: false in order to avoid this. Otherwise, you’ll get the following error when starting the refactor:
{
"StackRefactorId": "fa44d308-c060-4b40-bb9a-075230edeaf3",
"StackIds": [
"BucketStack"
],
"ExecutionStatus": "UNAVAILABLE",
"Status": "CREATE_FAILED",
"StatusReason": "arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/BucketStack/ec6f69ee-2ce7-4a32-b7fb-d11b104c480c: Following template sections are not allowed when creating a stack while refactoring: Conditions, Rules"
}
So when you’re instantiating the BucketStack, pass in a custom synthesizer like this to avoid creating the CDK Bootstrap Rule resource:
new BucketStack(app, 'BucketStack', {
// `Rule` resources are not allowed during refactoring. This can be removed after the refactor completes.
synthesizer: new cdk.DefaultStackSynthesizer({
generateBootstrapVersionRule: false,
}),
allowedPrincipal: stack.instanceRole
})
This takes care of the Rule resource, but you’ll also need to pass flags to cdk deploy and cdk synth to avoid creating the Condition resources. See below.
Step 3: Create the Resource Mapping
The “resource mapping” is a JSON document which tells CloudFormation which resources are moving and which stacks are involved in the refactor. Here is what ours will look like in this example:
[
{
"Source": {
"StackName": "StackRefactorStack",
"LogicalResourceId": "Bucket83908E77"
},
"Destination": {
"StackName": "BucketStack",
"LogicalResourceId": "Bucket83908E77"
}
}
]
This is pretty self-explanatory, but it just declares that we’re moving the Bucket identified by Logical Resource ID Bucket83908E77 to the BucketStack from the StackRefactorStack. The easiest way to find the logical resource ID of your bucket is to look in the generated CloudFormation template:
$ grep -B1 'AWS::S3::Bucket' cdk.out/StackRefactorStack.template.json
"Bucket83908E77": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
Synthesize the stacks
The modified stacks need to be synthesized in order to create the stack refactor task. We’re going to pass in some extra flags here to avoid creating resources which the stack refactor does not support:
cdk synth --version-reporting=false --path-metadata=false --asset-metadata=false
Submit the stack refactor
Now we’re going to submit the resource mapping we created earlier – I named mine refactor.json – to the CloudFormation API using the create-stack-refactor API. It’s important to note that this won’t actually perform the refactor, it just stages the change so that you can run it later with execute-stack-refactor.
aws cloudformation create-stack-refactor \
--stack-definitions \
StackName=BucketStack,TemplateBody@=file://cdk.out/BucketStack.template.json \
StackName=StackRefactorStack,TemplateBody@=file://cdk.out/StackRefactorStack.template.json \
--enable-stack-creation \ # Omit this flag if you're moving the resource to an existing stack
--resource-mappings file://refactor.json
This will output a stack refactor ID which you’ll use to describe the status of the refactor and see if there are any issues before you perform the refactor.
{
"StackRefactorId": "2e854a07-73b0-42d1-8077-384ce2635583"
}
If the refactor was created successfully, the status of the refactor should be CREATE_COMPLETE:
$ aws cloudformation describe-stack-refactor --stack-refactor-id 2e854a07-73b0-42d1-8077-384ce2635583
{
"StackRefactorId": "2e854a07-73b0-42d1-8077-384ce2635583",
"StackIds": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/StackRefactorStack/fd2b1b20-e7cc-11ef-a316-06ca57e568d9",
"arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/BucketStack/31e55930-e7d1-11ef-90e2-0a407e496199"
],
"ExecutionStatus": "AVAILABLE",
"Status": "CREATE_COMPLETE"
}
Mine was failing on my first few attempts because I wasn’t passing in the “before” stack in the stack definitions. It gave me an error like The resource Bucket83908E77 defined in the resources mapping did no move from its original stack StackRefactorStack. Review your stack template desired state. and all I had to do to fix that was make sure I passed in both stacks to the --stack-definitions.
Step 4: Execute the Stack Refactor
With all of the annoying prep work out of the way, executing the refactor itself should be the easy part. Take the refactor ID from before, and run execute-stack-refactor.
aws cloudformation execute-stack-refactor --stack-refactor-id 2e854a07-73b0-42d1-8077-384ce2635583
Now you can track the status of the refactor by calling describe-stack-refactor again. When the execution is complete, you’ll see the following output:
$ aws cloudformation describe-stack-refactor --stack-refactor-id 2e854a07-73b0-42d1-8077-384ce2635583
{
"StackRefactorId": "2e854a07-73b0-42d1-8077-384ce2635583",
"StackIds": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/StackRefactorStack/fd2b1b20-e7cc-11ef-a316-06ca57e568d9",
"arn:aws:cloudformation:us-east-2:123456789012:stack/BucketStack/31e55930-e7d1-11ef-90e2-0a407e496199"
],
"ExecutionStatus": "EXECUTE_COMPLETE",
"Status": "CREATE_COMPLETE"
}
Hooray! The S3 bucket is now in the new stack. I’m very grateful for this new feature… it’s nice knowing that I’m no longer stuck living with my poor decisions from 5 years ago. I think there’s still a lot of improvement to go before this gets anywhere near the level of flexibility you have in state management with Terraform, but I’ll take it. Here is what the update looked like for me in the CloudFormation UI once all was said and done.
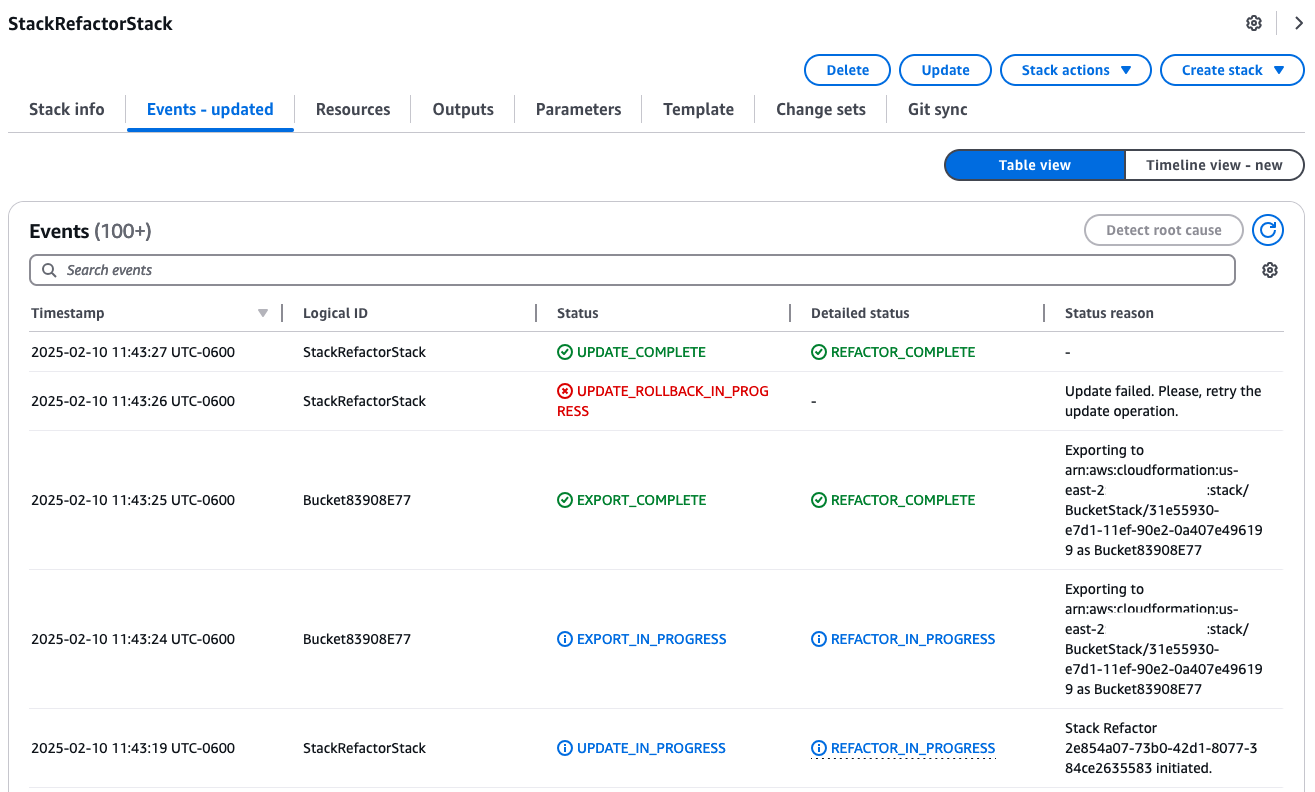
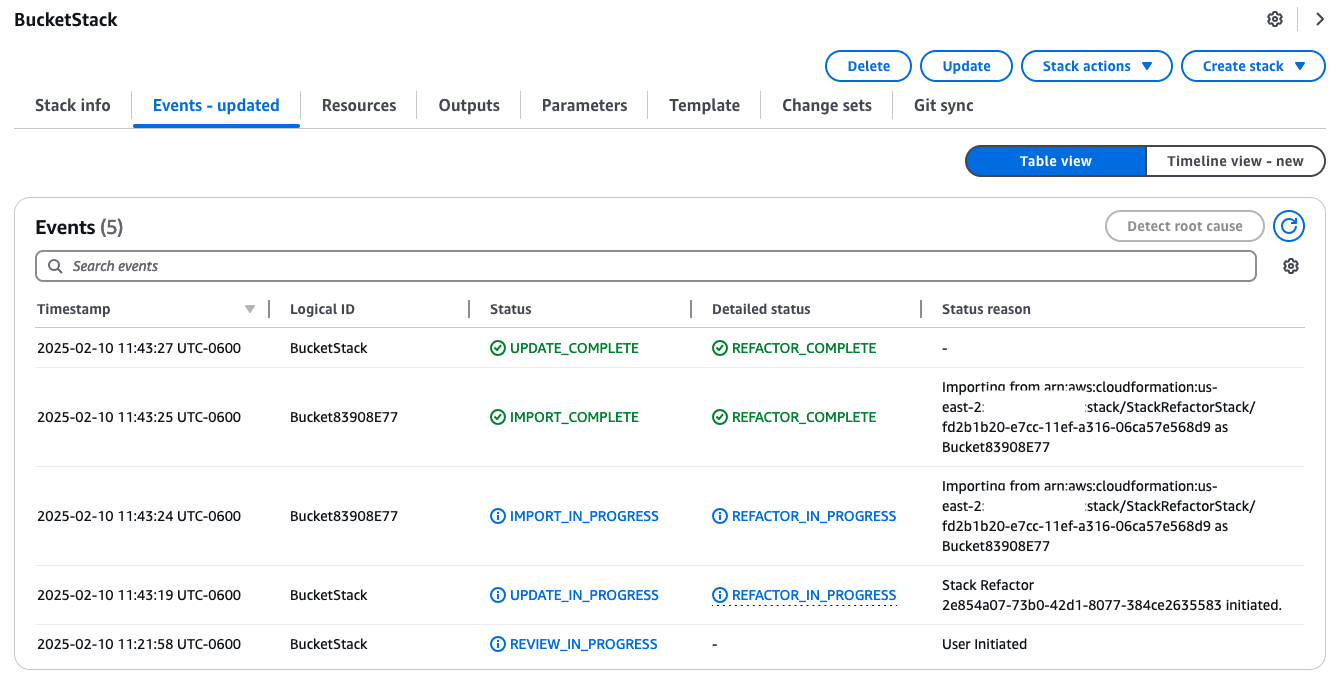
tl;dr
- Redeploy “before” stack without unsupported metadata resources.
cdk deploy --version-reporting=false --path-metadata=false --asset-metadata=false -e StackRefactorStack - Make changes in CDK, be sure to set
generateBootstrapVersionRule: falsewhen instantiating the new stack. (more info) - Synthesize new templates.
cdk synth --version-reporting=false --path-metadata=false --asset-metadata=false - Create the JSON resource mapping to indicate which resource is moving between which stacks. (more info)
- Create stack refactor task.
aws cloudformation create-stack-refactor --stack-definitions StackName=BucketStack,TemplateBody@=file://cdk.out/BucketStack.template.json StackName=StackRefactorStack,TemplateBody@=file://cdk.out/StackRefactorStack.template.json --enable-stack-creation --resource-mappings file://refactor.json - Execute refactor.
aws cloudformation execute-stack-refactor --stack-refactor-id $REFACTOR_ID